According to an analysis by the Korean Intellectual Property Office (KIPO), a total of 5,525 patent applications for robots integrating artificial intelligence (AI) technology were filed in the IP5 countries (Korea, the United States, China, the European Union and Japan). Over the past decade (2012-2021), the number of these applications grew at an average annual rate of 58.5%, rising sharply from just 20 filings in 2012 to 1,260 in 2021.
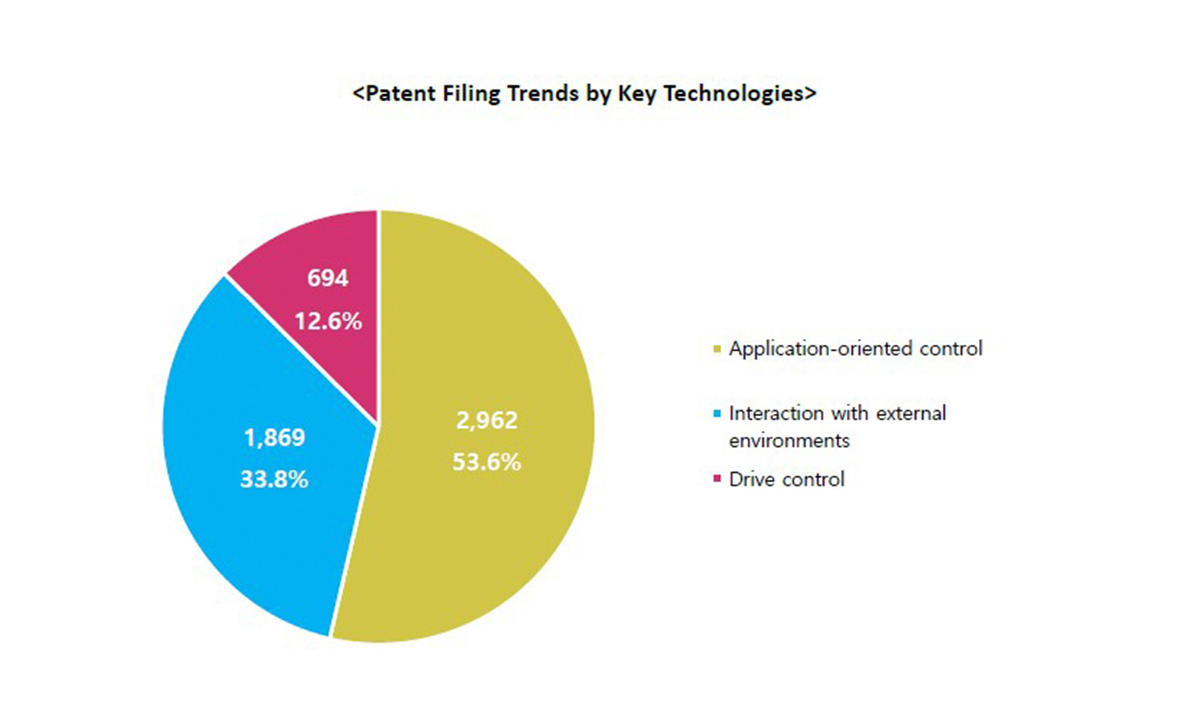
A breakdown of the AI-integrated technologies shows that application-oriented control technologies, where robots are deployed in fields such as education, entertainment and healthcare, comprised the largest share at 53.6% (2,962 applications). Technologies for interaction with external environments, enabling robots to recognize and manipulate objects, accounted for 33.8% (1,869 applications), while drive control technologies, which control robot movements through machine learning, made up the remaining 12.6% (694 applications).
In terms of applicant nationality, China led with 60% of the total filings (3,313 applications), followed by Korea with 24.7% (1,367 applications) and the United States with 8.1% (46 applications). China also recorded the highest average annual growth rate in filing at 59.7%, with Korea following at 53.4%.
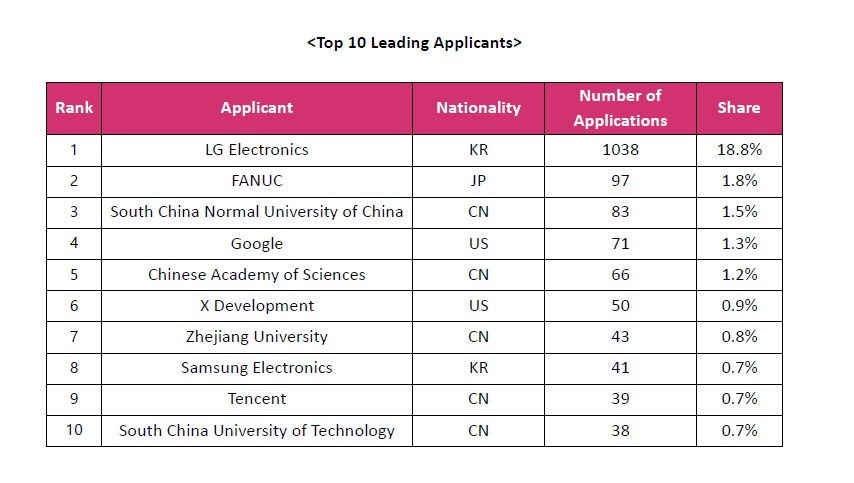
LG Electronics emerged as the top applicant, accounting for 18.8% (1,038 applications) of the total applications. It was followed by Japan’s FANUC with 1.8% (97 applications) and China’s South China Normal University with 1.5% (83 applications). The data indicates that LG Electronics has been actively securing patent protection both domestically and internationally, particularly for AI-integrated technologies such as object recognition and voice recognition applied in cleaning, service and logistics robots. In addition, Korea’s Samsung Electronics ranked eighth with 0.7% (41 applications), highlighting the strong growth potential of Korean companies in the AI robotics industry. The top 10 leading applicants are shown in the table below:
According to KIPO, the patent applications filed by Chinese companies are primarily limited to domestic filings, while major global tech companies, such as Tesla, have so far filed relatively few applications in this field. As a result, companies that proactively pursue patent protection for core AI robot technologies, including interaction with external environments, (e.g., object recognition, manipulation and multimodal interfaces), as well as learning and control technologies for robot driving, are expected to secure early and strategic patent rights. This presents a valuable opportunity in a rapidly growing sector expected to expand significantly in the coming years.